LESSON 11.1 | SHOULD, SHOULDN'T
Should
English Grammar - Modal
Verbs
Should is a
modal verb.
After Should you use the base form
of the infinitive (= verb without To e.g. Go instead
of To Go)
Should + Verb (base form of infinitive)
e.g. You should go now (do not
say: You should to go now.)
SHOULD
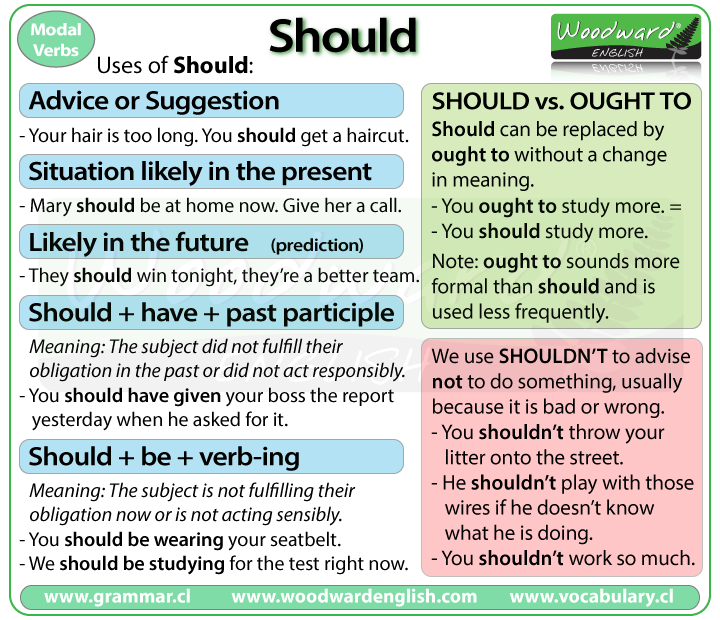
1. To give advice, a recommendation or a suggestion
This is to say that it is the right thing to do or
the correct thing.
- Does your tooth still hurt? You should make
an appointment with the dentist.
- I think you should study
for the test so that you don't fail.
- Your hair is too long. You should get
a haircut.
- You really should go to
the new restaurant on Main Street.
2. Expresses that a situation is likely in the
present
- Mary should be at home
by now. Give
her a call.
- He should have the letter
by now. I sent it a couple of weeks ago.
3. Expresses that a situation is likely in the
future (prediction)
- They should win the
game because they are a much better team.
- I posted the cheque yesterday so
it should arrive this week.
- It should be fine
tomorrow.
4. Expresses an obligation that is not as strong
as Must.
Sometimes Should is used instead
of Must to make rules, orders or instructions sound more
polite. This may appear more frequently on formal notices or on information
sheets.
- On hearing the fire alarm, hotel
guests should leave their room immediately.
- Passengers should check
in at least 2 hours before departure time.
- You should never lie to
your doctor.
- You should pay more
attention in class.
- You should be at work
before 9.
All of the above example sentences can have must instead
of should making the obligation stronger and less polite.
5. Was expected in the past but didn't happen
(should + have + past participle)
This expresses the idea that the subject did not
fulfill their obligation in the past or did not act responsibly.
- You should have given
your boss the report yesterday when he asked for it.
- I should have studied
more but I was too tired.
6. Not fulfilling an obligation (should + be +
verb-ing)
This expresses the idea that the subject is not
fulfilling their obligation or is not acting sensibly.
- You should be wearing your
seatbelt. (The person isn't wearing one right now)
- We should be studying for
the test. (We are not studying right now and we should)
7. Sometimes should is replaced
by ought to without a change in meaning. Note that ought
to sounds more formal and is used less frequently.
- You ought to study
more. (=
you should study more)
- He ought to go home. (= He should go
home)
- They ought to stop
doing that. (= They should stop doing that)
Shouldn't
We use shouldn't to advise not to do something,
usually because it is bad or wrong to do.
- You shouldn't throw
your litter onto the street.
- We shouldn't leave
without saying goodbye.
- He shouldn't play with
those wires if he doesn't know what he is doing.
- Are you tired? You shouldn't work
so much.
- You shouldn't talk like
that to your grandmother.
Should Summary Chart

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario