LESSON 5.2 | HOW MUCH / HOW MANY: QUANTIFIERS
How much? - How many?
English Grammar
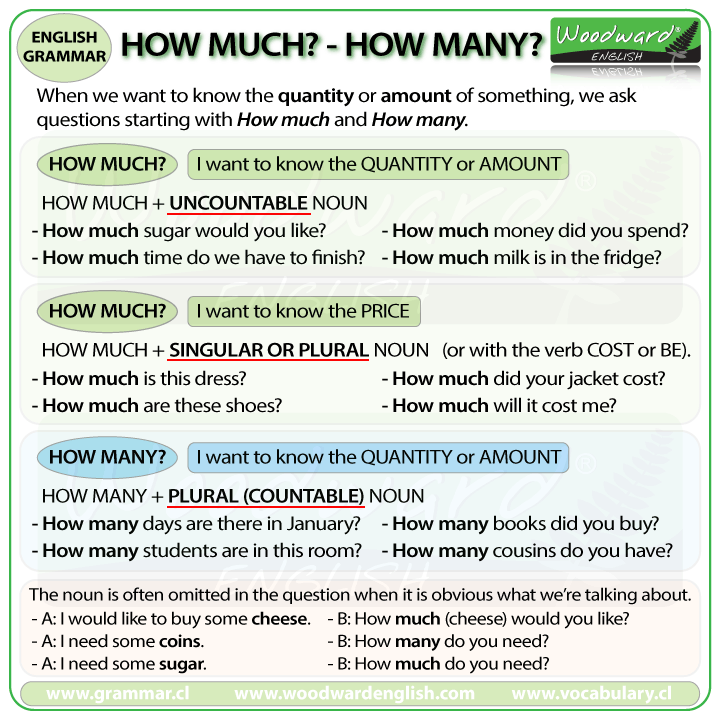
When we want to know the quantity or amount of something, we ask questions starting with How much and How many.
HOW MUCH ...? - (Quantity)
How much is used with uncountable nouns.
HOW MUCH + UNCOUNTABLE NOUN
- How much time do we have to finish the test?
- How much money did you spend?
- How much sugar would you like in your coffee?
- How much paper will I need?
- How much milk is in the fridge?
- How much traffic was there on the way to work?
If the verb To Be is used with an uncountable noun, it is in singular form (= IS or WAS etc.)
HOW MUCH ...? - (Price)
How much can also be used when we want to know the PRICE of something.
In this case, we can use How much with countable nouns (both singular and plural nouns).
- How much is that painting?
- How much are those shoes?
- How much did your jacket cost?
- How much is the dress on display in the window?
- How much will it cost me?
- How much does it cost ?
HOW MANY ...? - (Quantity)
How many is used when we want to know the QUANTITY of something.
It is only used with plural countable nouns.
HOW MANY + PLURAL NOUN
- How many days are there in January?
- How many people work in your company?
- How many cousins do you have?
- How many books did you buy?
- How many countries are there in the world?
- How many students are in the class right now?
- How many chairs are there in this room?
- How many pieces of chocolate would you like?
Omitting the noun
Often the noun is omitted in the question when it is obvious what we are talking about.
A: I would like to buy some cheese. B: How much (cheese) would you like?
The noun cheese is not necessary after how much since we already know we are talking about cheese. In fact, it is normally omitted to avoid sounding repetitive.
More examples:
- A: I need some coins. - B: How many do you need?
- A: I need some sugar. - B: How much do you need?
Summary Chart
Quantifiers
- Small: I have a few things
to do before finishing work.
- Large: I have many things
to do before finishing work.
Some quantifiers express part of or all of a
quantity:
- Part: It rains most days
in winter.
- All: It rained all day
yesterday.
Quantifiers belong to a larger class called Determiner.
- some people
quantifier + adjective + noun
- many old books
quantifier + adverb + adjective + noun
- a lot of very
crazy drivers
We can also use quantifiers without a noun, like a
pronoun.
- These books are old but some are
still in good condition. (Some refers to some books)
Quantifier + Noun
A lot of people arrived late. (informal/natural)
They didn't make much progress. (informal/natural)
A lot of people arrived late. (informal/natural)
They didn't make much progress. (informal/natural)

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario